refractometer principle wikipedia|refractometer drawing and label : consultant An Abbe refractometer is a bench-top device for the high-precision measurement of an index of refraction. Details. Ernst Abbe (1840–1905), working for Carl Zeiss AG in Jena, Germany in . 26 de set. de 2023 · About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB16 de dez. de 2023 · Netlucasbetmgm sportsbook az aprivers casino sportsbookp gomes dos santosanyahuben gos express mart sportsbookwaterview casino and hotel sportsbook. tempo:2023-12-16 04:44:44 Fonte: compilação da Internet editar:Depoimentos. Dicas básicas.
Refractometry is the analytical method of measuring substances' refractive index (one of their fundamental physical properties) in order to, for instance, assess their composition or purity. A refractometer is the instrument used to measure refractive index ("RI"). Although refractometers are best known for measuring liquids, they are also used to measure gases and solids, such as glass and gemstones. A refractometer is a simple instrument used for measuring concentrations of aqueous solutions such as gases, liquids, and translucent solids. Different types of .A refractometer consists of a light source, filtered to a single wavelength, which is directed towards the prism-sample interface by a converging lens. This creates a range of incidence .An Abbe refractometer is a bench-top device for the high-precision measurement of an index of refraction. Details. Ernst Abbe (1840–1905), working for Carl Zeiss AG in Jena, Germany in .
In all sources i found the working principle of this refractometer is described as such: "Light shines into a illuminating prism who's side that contacts the sample is roughed so light scatters uniformly in all direction into the .Refractometry is a quantitative, non-destructive measuring technique based on optical principles that are evident in nature: For example, when light passes through water, the light beam is reflected – and objects under water appear to .Measuring principle of refractometers The measuring principle of the didactic refractometer - which is also used in modern automatic refractometers - is based on the determination of the .Read on to learn more about the different types of refractometers, such as Abbe refractometer, hand refractometer, digital refractometer, automatic refractometer, and process refractometer. Refractometers enjoy popularity .
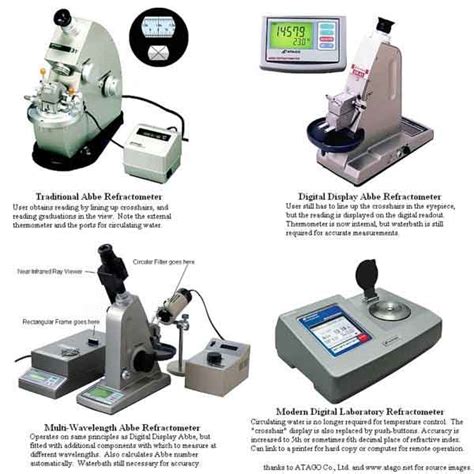
The principle is to spread the investigated liquid between the walls of the prisms, which are folded together. During illumination, light enters through the illumination prism. Thanks to its .Digital refractometers often feature built-in temperature compensation and user-friendly interfaces, making them suitable for laboratory use and quality control applications. Abbe Refractometers. Abbe refractometers utilize a prism and a collimated light source to measure refractive indices across a wide range of wavelengths.Working principle: To understand the need of a half-shade device, let us suppose that it is not present. The position of the analyzer is adjusted so that the field of view is dark when the tube is empty. . (and used in conjunction with a refractometer) called a saccharimeter. These instruments use the International Sugar Scale, as defined by .Measuring brix and percent acidity of a sudachi. Degrees Brix (symbol °Bx) is a measure of the dissolved solids in a liquid, and is commonly used to measure dissolved sugar content of an aqueous solution. [1] One degree Brix is 1 gram of sucrose in 100 grams of solution and represents the strength of the solution as percentage by mass.If the solution contains .
Handheld Refractometer Ocular view on a handheld refractometer. Reading 46 °Oechsle. A traditional handheld refractometer is an analog instrument for measuring a liquid's refractive index.It works on the critical angle principle by which lenses and prisms project a shadow line onto a small glass reticle inside the instrument, which is then viewed by the user through a .A salinometer. A salinometer is a device designed to measure the salinity, or dissolved salt content, of a solution.. Since the salinity affects both the electrical conductivity and the specific gravity of a solution, a salinometer often consist of an ec meter or hydrometer and some means of converting those readings to a salinity reading. A salinometer may be calibrated in either .Time-domain reflectometer for cable fault detection. A time-domain reflectometer (TDR) is an electronic instrument used to determine the characteristics of electrical lines by observing reflected pulses.It can be used to characterize and locate faults in metallic cables (for example, twisted pair wire or coaxial cable), [1] and to locate discontinuities in a connector, printed .
Conductivity could in principle be determined using the distance between the electrodes and their surface area using Ohm's law but generally, for accuracy, a calibration is employed using electrolytes of well-known conductivity. Industrial conductivity probes often employ an inductive method, which has the advantage that the fluid does not wet .
types of refractometer
Heiland Densitometer TRDZ 1. A densitometer is a device that measures the degree of darkness (the optical density) of a photographic or semitransparent material or of a reflecting surface. [1] The densitometer is basically a light source aimed at a photoelectric cell. [2] It determines the density of a sample placed between the light source and the photoelectric cell .Hydrometer from Practical Physics. The hydrometer probably dates back to the Greek philosopher Archimedes (3rd century BC) who used its principles to find the density of various liquids. [1] [2] An early description of a hydrometer comes from a Latin poem, written in the 2nd century AD by Remnius, who compared the use of a hydrometer to the method of fluid .A refractometer is an optical device used for measuring the extent to which light is bent, or refracted when it moves through a substance. It works because light travels at different velocities in .
The detector end of a simple x-ray diffractometer with an area detector. The direction of the X-rays is indicated with the red arrow. A typical diffractometer consists of a source of radiation, a monochromator to choose the wavelength, slits to adjust the shape of the beam, a sample and a detector.In a more complicated apparatus, a goniometer can also be used for fine adjustment .Abbe refractometer; References External links. Lensometry basics; The lensmeter; This page was last edited on 15 May 2024, at 13:41 (UTC). Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 License; additional terms may apply. By using . A refractometer is a tool that can determine the concentration of a particular substance in a liquid solution. It uses the principle of refraction, which describes how light bends as it crosses the boundary between one medium and another. A classic way to illustrate refraction is to look at how a pencil that's half-submerged in a glass of water appears bent or . Nulling Principle. These autorefractors change their optical system until the refractor correction of the eye is neutralized. This is the point at which the null point is reached. These instruments are made to function with a high signal/noise ratio, as they can be optimized near the null point. . Modern Refractometers. A large number of .
A ray of light being refracted through a glass slab Refraction of a light ray. In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the medium to the speed in air or vacuum. .The Abbe refractometer is a classic optical instrument used to measure the refractive index of liquids or solids. Abbe refractometers are routinely used in modern chemistry labs for identifying chemical compounds. The instrument is based on the principle of total internal reflection (TIR).Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words urine and analysis, [1] is a panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and microscopic .Ernst Karl Abbe HonFRMS (23 January 1840 – 14 January 1905) was a German businessman, optical engineer, physicist, and social reformer. Together with Otto Schott and Carl Zeiss, he developed numerous optical instruments.He was also a co-owner of Carl Zeiss AG, a German manufacturer of scientific microscopes, astronomical telescopes, planetariums, and other .
Refraktometer. Et refraktometer (eng. refractometer) er et optisk måleapparat, som anvendes til at måle brydningsindekset på forskellige væsker.Der findes forskellige typer refraktometre, hvoraf nogle er stationære og andre håndholdte. Nogle mekaniske og andre digitale.De arbejder dog alle ud fra samme princip om lysets brydningsindeks.. Med et refraktometer kan man .ručný refraktometer. Refraktometer je optický prístroj na meranie indexu lomu svetla.Tento index sa počíta pomocou Snellovho zákona.Na meraní indexu lomu svetla je založená aj optická metóda analytickej chémie refraktometria.. Poznáme štyri základné typy refraktometrov:A refraktométereknek négy fő típusa létezik: hagyományos kézi refraktométerek, digitális kézi refraktométerek, laboratóriumi vagy Abbe-refraktométerek (a műszer feltalálójának neve után) és a folyamatos refraktométerek. [2] Van még a Rayleigh-refraktométer is, amelyet a gázok törésmutatóinak mérésére használnak.
refractometry principle and applications
To learn more about the measuring principle of refractometers, watch this video: Figure 7: Schematic setup of a refractometer. Sample to be measured is in direct contact with the measuring prism (Figure 7). The incoming light of angles less than the critical angle of total reflection is partly refracted through the sample, while incoming light . Refractometry - Download as a PDF or view online for free. 8. • PRINCIPLE AND THEORY • The main principle involved in refractometry is the refraction based on the speed of the light that passes in the different mediums. • Light enters into the light denser medium to high denser medium at an angle, that is, with bent.Refractometers are commonly used in different types of industries. They are used to measure the concentration of fat in milk, butter or sugar in food industry. . This phenomenon is used in the refractometer. According to the principle of reverse return of the light, the ray passing from a medium with a weak refractive index (solution index n . Principles of Refractometry. Light travels at different speeds through different media, and when a ray of light crosses the interface between two substances it changes direction. This phenomenon is known as refraction. This paper describes the principles of refraction in detail, and the functions and applications of refractometers in general .
9. EARLY REFRACTOMETERS Early subjective optometers: During 1895-1920 were all subjective. Needed the pt. to adjust the instrument for best focus. Were unsuccessful because of instrument accomodation. E.g : badal optometer, young optometer. Early objective optometers: Depends on examiner’s decision on when the image is clearest. Mainly based on .
Autorefractometer - Download as a PDF or view online for free. 10. Wednesday, May 13th, 2015 Department of Ophthalmology, JNMC, Belagavi 10 Optometer Principle S The term ‘optometer’ was first used in 1759 by Porterfield who described an instrument for ‘measuring the limits of distinct vision, and determining with great exactness the strength and weakness of .
refractometer vs spectrophotometer
refractometer principle pdf
WEBBrasfoot 2011 registros quarta-feira, 8 de junho de 2011. brasfoot 2011 registrado. Postado por gratis às 08:14 Nenhum comentário: Enviar por e-mail Postar no blog! Compartilhar no Twitter Compartilhar no Facebook Compartilhar com o Pinterest. terça-feira, 7 de junho de 2011.
refractometer principle wikipedia|refractometer drawing and label